Configuring BitFire Bot Control
version 3.5.1+
BitFire Bot Control configuration guide
About Web Scanners and Bots
Automated web scanners, also known as web crawlers or bots, are essential tools for many legitimate online activities, such as search engine indexing and online price comparison. However, these scanners can also be used for malicious purposes, such as scraping sensitive information, launching DDoS attacks, or even spreading malware. As a result, it is important to block automated web scanners in order to protect both personal and organizational information and systems.
In addition to scraping sensitive information, automated web scanners are used for DDoS attacks. These scanners can be used to flood a website with a large number of requests, overwhelming the server and causing the website to go offline. This can disrupt business operations and damage a company's reputation.
Automated web scanners can also be used to spread malware. These scanners can be programmed to search for vulnerabilities in websites and systems, and then exploit them to install malware or launch an attack. This can cause significant damage to both personal and organizational information and systems.

What Is BitFire Bot Control?
The Bot Control page in the BitFire dashboard allows you to control exactly how to handle each robot. There are many thousands of automated crawlers, tools, scanners bots and many other automated systems accessing web sites on the Internet. Many of these bots are benign and helpful, some are not.
BitFire's remote API maintains a list of several thousand bots. Each of these bots has network authentication information which is used to securely identify each bot. Secure network identification identifies the source network for the request, this ensures that bots claiming to be "GoogleBot" are only allowed from Google IP addresses, and not Romania or Colombia, etc.
How Does It Work?
By default, BitFire will allow all known benign bots that have secure network authentication. Any time a new bot is seen accessing the website, BitFire authenticates the bot and if the secure auth check passes the bot is allowed.
During the learning phase in the first 5 days of operation, any bot BitFire sees will be added to the allow list from the same origin network. This feature ensures that any unknown web tool or third party service will still be allowed access once the Firewall is in full block mode.
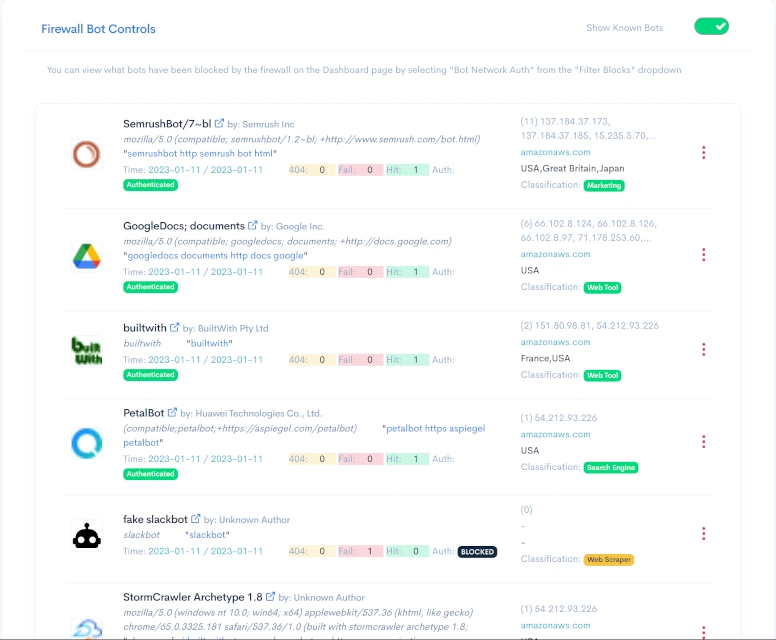
Understanding the Bot Control Page
The bot control page contains a lot of information about each bot accessing your website. You can switch between known bots and unknown bots by selecting the "Show Known Bots" toggle switch. All bots are sorted in the order they were last seen.
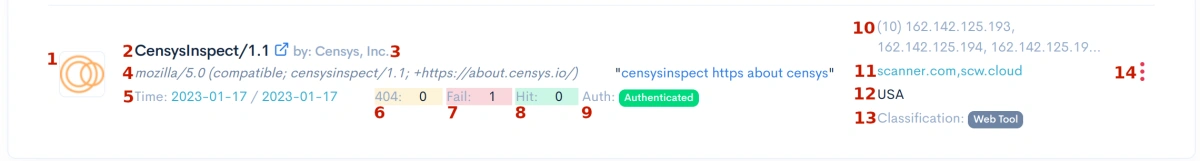
- 1: The bot icon if the bot is identified. Your first indicator the bot is not malicious
- 2: The bot identified bot name. Clicking on the name will take you to a webpage with additional info.
- 3: The bot vendor name.
- 4: Complete User Agent sent by the bot.
- 5: The first time the bot was seen, and the last time it was seen.
- 6: Number of invalid page requests. A high number indicates malicious.
- 7: Number of requests that failed network authentication.
- 8: Number of requests that passed network authentication.
- 9: Green - Validate Network Authentication. Black - blocked. Red - Allow from Anywhere.
- 10: The first 30 IP addresses seen using this bot's User-Agent
- 11: The domain networks valid for secure authentication
- 12: List of origin countries bot was seen from
- 13: Internal classification if known
- 14: Bot control button. Click to change this bot handling.
Using Bot Control Effectively
To effectively use the bot control provided by BitFire you should review the the known and unknown bot pages after Firewall learning is complete. Take a moment to go through the list. Make sure that any third party tools or services that you use are set to either "Authenticated" or "ANY IP". Most bots and services can be restricted to authenticated IPS and networks, but some services may not have static networking and must be set to "ANY IP".
Be careful when configuring any bot to allow "ANY IP" as this will allow anyone anywhere on the planet to use this User-Agent to bypass your bot filtering. The more well known the bot (think GoogleBot, Bing, etc) the more likely setting this to "ANY IP" could result in abuse. If is very unlikely for an attacker to set their User-Agent to "Bob's Unkown Third Party Tool" in hopes of bypassing Firewall Filtering. The most likely case for abuse is popular search engines.
Allowed Bots Are Still Firewalled
It is important to note, that even if a bot is allowed in Bot Control, the BitFire firewalling features are still run. This includes, XSS, SQLi, CSRF, SSRF, XXE, and other firewall features. Bot Control is intended to block scanners looking for unknown or difficult to detect abuse from completing their scans.